Clear Text Protocols VS Cryptographic Protocols
A clear text protocol is used to transmit data without any form of encryption. If you are sending data from a host to a server, the data appears in clear text and can easily be eavesdropped by a malicious person, using a packet sniffing tool (Wireshark). Such protocol should only be used on trusted networks. An example of a clear text protocol is http.
A cryptographic protocol is used to transmit data with encryption. Therefore, it prevents eavesdropping: the transmitted data can't be read. An example of cryptographic protocol is https.
Another possibility is to tunnel a clear text protocol with a cryptographic protocol. This method is used by Virtual Private Networks. A VPN extends a private network over a public one using cryptography tunneling (such as the Internet). Therefore, it establishes a protected connection to a private network and uses the protocols of private networks. Using a VPN is the equivalent of being directly connected to the private network. Here is an illustration for you to better understand:
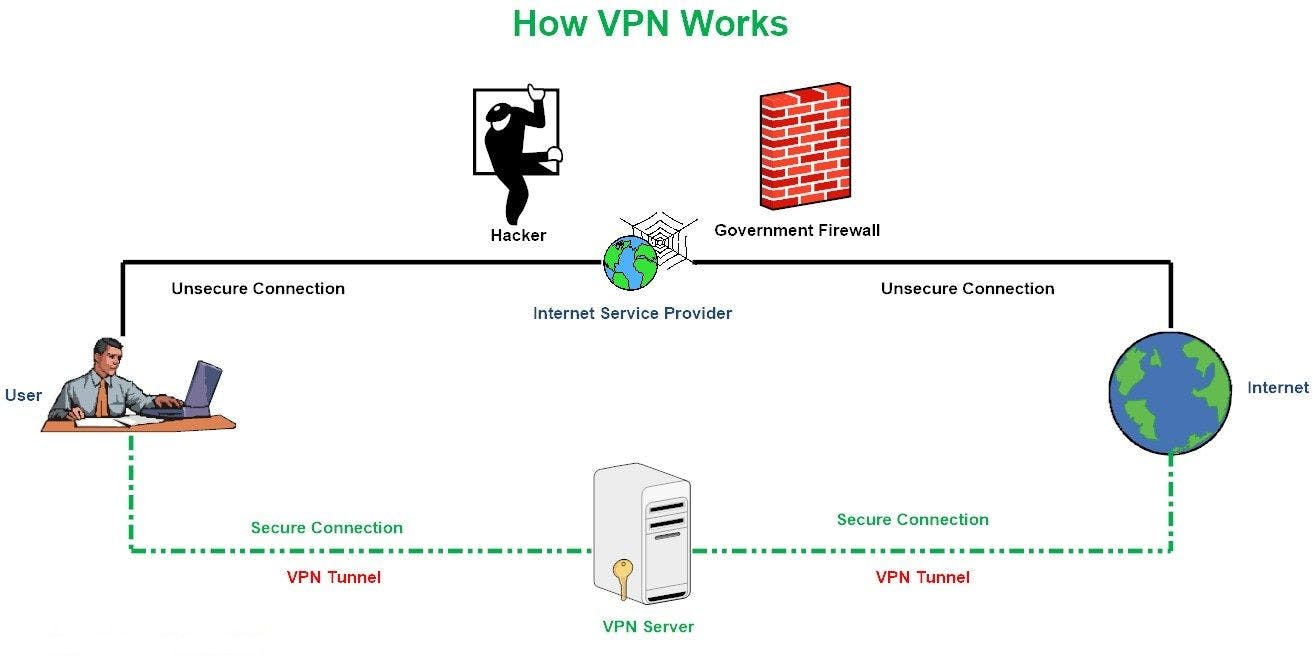
You have probably heard that VPNs have the ability to change the IP adress of your host when navigating on the Internet. In fact, your IP adress isn't modified (an IP adress is unique), the VPN simply replaces your IP adress with the one of the VPN server you are connected to. This is why you can choose your online location with a virtual private network, depending on the VPN server's location in the world.
Now that you know that a VPN uses a cryptographic protocol to tunnel the transmitted informations, here are some example of these protocols:
OpenVPN: OpenVPN is one of the most widely used VPN protocols. It is an open source protocol that uses encryption based on the OpenSSI and SSLv3.TLSv1 protocols.
IPSec/L2TP: This protocol combines IPsec for data encryption with L2TP for secure connection. Most operating systems include IPsec/L2TP.
IKEv2/IPSec: It is a protocol based on IPSec. This protocol allows you to quickly connect and switch between networks. It is an ideal choice for smartphones, as these devices tend to switch regularly between WiFi and public WiFi networks.
PPTP: Point-to-Point tunnel protocol was one of the first protocols available. This protocol contains some potential leaks. Therefore, I won't recommend you using it unless speed is more important for you than security. This protocol is adapted if you want to bypass restrictions set by streaming services.
WireGuard: WireGuard is a relatively new protocol that is gaining more attention. It runs on a Linux kernel and competes with OpenVPN and IPsec.
- SSTP: SSTP can be seen as Microsoft creating a fitting replacement for PPTP.
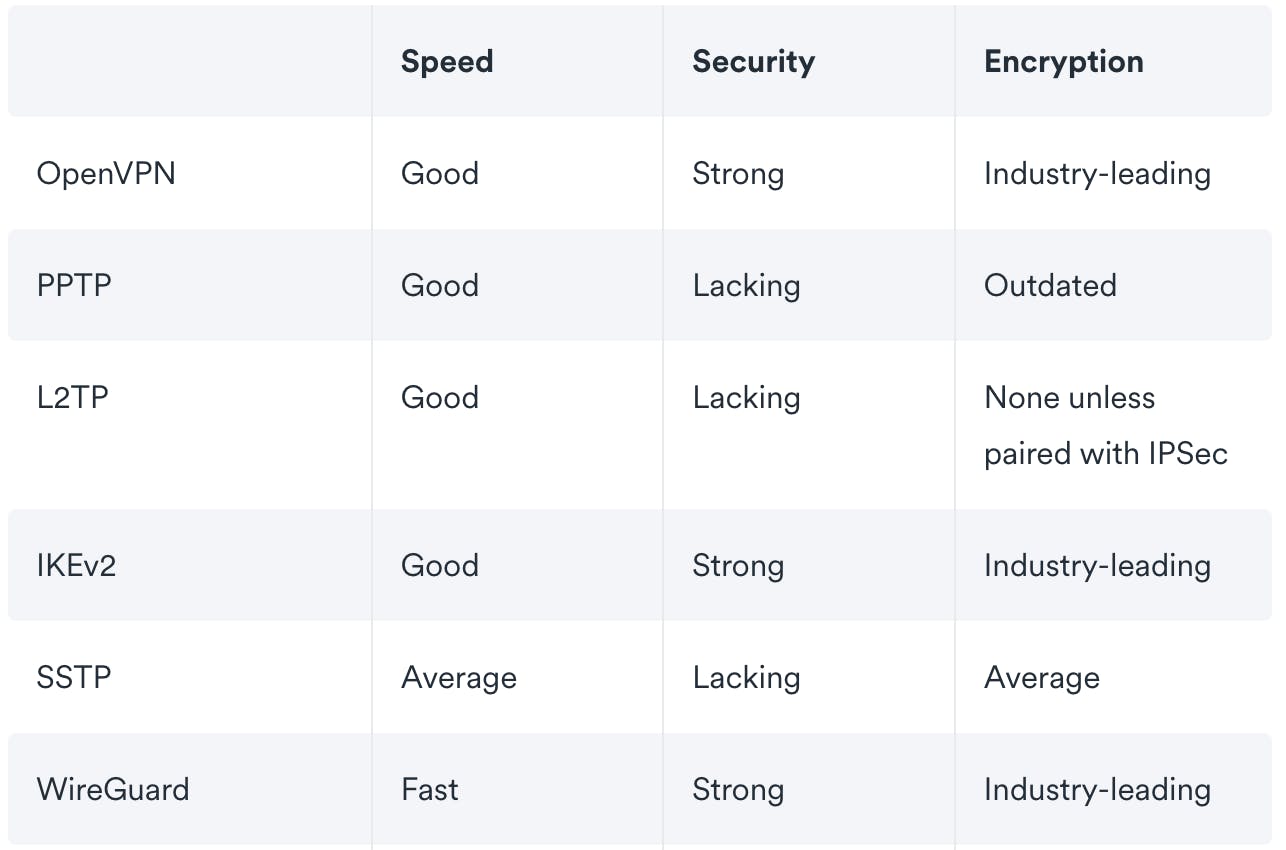
VPN protocols Comparison